Exploring the Top 10 Trends in Health Information Technology for 2025 opens a window into the advancements that will shape the healthcare landscape in the coming years. From AI to blockchain, these trends are poised to revolutionize patient care and data management.
Let's dive in and uncover the potential impact of these emerging technologies.
Overview of Health Information Technology Trends for 2025
Tracking trends in health information technology is crucial in today's rapidly evolving healthcare landscape. As technology continues to advance, staying informed about the latest trends in healthcare IT is essential for healthcare professionals, organizations, and patients alike.
Staying updated with the latest trends in the healthcare industry allows for improved patient care, streamlined processes, enhanced data security, and increased efficiency. It also enables healthcare providers to adopt new technologies that can ultimately lead to better health outcomes for patients.
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, telemedicine, blockchain, and Internet of Things are shaping the future of healthcare IT. These technologies have the potential to revolutionize the way healthcare is delivered, making it more personalized, accessible, and efficient. By embracing these trends, healthcare organizations can stay ahead of the curve and provide cutting-edge care to their patients.
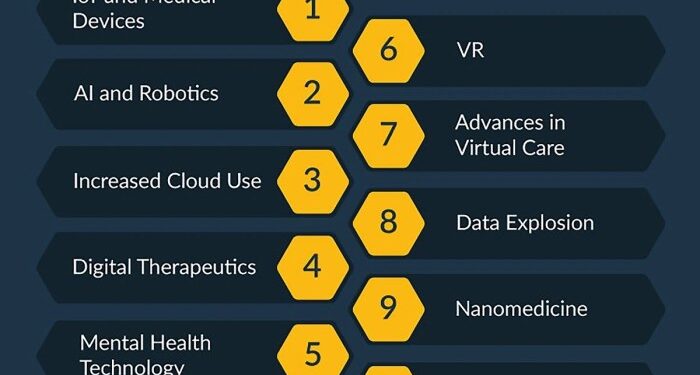
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Healthcare
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning have been instrumental in transforming healthcare practices by offering innovative solutions to improve patient care and outcomes. These technologies have the potential to revolutionize the way healthcare providers diagnose, treat, and manage various medical conditions.
Applications of AI in Health Information Technology
- Medical Imaging Analysis: AI algorithms can analyze medical images such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans to assist radiologists in detecting abnormalities and making accurate diagnoses.
- Predictive Analytics: AI can analyze large datasets to predict disease progression, identify high-risk patients, and personalize treatment plans for better outcomes.
- Natural Language Processing: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can interact with patients, answer queries, and provide personalized health information.
- Drug Discovery and Development: Machine learning algorithms can accelerate the drug discovery process by analyzing molecular structures and predicting potential drug candidates.
Improving Patient Care and Outcomes with AI and Machine Learning
- Enhanced Diagnosis: AI can help healthcare providers in early disease detection, leading to timely interventions and improved patient outcomes.
- Personalized Medicine: Machine learning algorithms can analyze patient data to create personalized treatment plans based on individual characteristics, genetics, and medical history.
- Remote Patient Monitoring: AI-enabled devices can monitor patients' health in real-time, alerting healthcare providers of any concerning changes and enabling timely interventions.
- Operational Efficiency: AI can streamline administrative tasks, optimize healthcare operations, and reduce healthcare costs, allowing providers to focus more on patient care.
Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) and Wearable Technology
The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) refers to a network of interconnected medical devices and applications that collect and share health data. This technology has a significant impact on the healthcare sector by enabling remote monitoring, improving patient outcomes, and enhancing the efficiency of healthcare delivery.
Wearable Technologies for Monitoring Health Data
Wearable technologies play a crucial role in IoMT by allowing individuals to track their health metrics in real-time. Some examples of wearable devices used for monitoring health data include:
- Fitness trackers: Devices like Fitbit and Apple Watch track physical activity, heart rate, and sleep patterns.
- Smart clothing: Garments embedded with sensors can monitor vital signs such as body temperature and respiratory rate.
- Blood glucose monitors: Wearable sensors help individuals with diabetes monitor their blood sugar levels continuously.
- Smart glasses: Glasses equipped with technology can provide real-time data and assist healthcare professionals during procedures.
Challenges and Benefits of Integrating IoMT into Healthcare Systems
Integrating IoMT into healthcare systems comes with both challenges and benefits:
- Challenges:
- Security concerns: Protecting sensitive health data from cyber threats is a significant challenge.
- Interoperability issues: Ensuring seamless communication between different devices and systems can be complex.
- Data overload: Managing the vast amount of data generated by IoMT devices requires advanced analytics and storage solutions.
- Benefits:
- Remote monitoring: IoMT enables healthcare providers to monitor patients remotely, improving access to care and reducing hospital visits.
- Personalized treatment: By analyzing real-time data, healthcare professionals can tailor treatment plans to individual patients' needs.
- Efficiency and cost savings: IoMT can streamline healthcare processes, leading to better resource utilization and reduced healthcare costs.
Telehealth and Remote Patient Monitoring
Telehealth services have revolutionized the way healthcare is delivered, providing patients with access to medical care remotely through digital communication technologies. This has significantly improved patient access and convenience, especially for individuals in rural or underserved areas who may have limited access to traditional healthcare facilities.
Role of Telehealth in Healthcare Delivery
- Telehealth allows patients to consult with healthcare providers through video calls, phone calls, or secure messaging, eliminating the need for in-person visits.
- Patients can receive medical advice, prescriptions, and follow-up care from the comfort of their homes, saving time and reducing travel costs.
- Telehealth services have become increasingly popular during the COVID-19 pandemic, enabling patients to receive care while minimizing the risk of exposure to the virus.
Remote Patient Monitoring for Chronic Conditions
- Remote patient monitoring involves the use of digital technologies to collect and transmit patient data to healthcare providers, allowing for real-time monitoring of chronic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease.
- Patients can use wearable devices to track their vital signs, blood glucose levels, or medication adherence, providing valuable data to healthcare professionals for timely intervention and personalized care.
- Remote patient monitoring helps in early detection of health issues, reduces hospital readmissions, and improves patient outcomes by enabling proactive management of chronic conditions.
Blockchain Technology in Health Information Management
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing the way health information is managed by providing a secure and decentralized platform for storing and sharing data. This innovative technology offers a transparent and tamper-proof system that enhances data security and integrity in healthcare.
Implementation of Blockchain to Secure Health Data
- Blockchain ensures the security and privacy of health data by using cryptographic techniques to create a secure and immutable ledger.
- Each block in the chain contains a unique cryptographic hash of the previous block, making it nearly impossible to alter or tamper with the data.
- Healthcare organizations are leveraging blockchain to securely store patient records, medical history, and sensitive information, reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
Potential Benefits of Blockchain in Improving Data Interoperability
- Blockchain technology has the potential to enhance data interoperability by providing a standardized and secure platform for sharing health information across different healthcare systems.
- By creating a decentralized network, blockchain allows for seamless and secure data exchange between healthcare providers, improving care coordination and patient outcomes.
- Smart contracts and permissioned blockchains enable automated and secure sharing of data, streamlining processes and reducing administrative burden.
Challenges and Concerns Associated with Integrating Blockchain in Healthcare
- One of the main challenges of integrating blockchain in healthcare is the scalability and processing speed of the network, as blockchain transactions can be slow compared to traditional databases.
- Regulatory concerns and compliance with data protection laws pose challenges for healthcare organizations looking to adopt blockchain technology for managing health information.
- Interoperability issues between existing healthcare systems and blockchain platforms may hinder the widespread adoption of this technology in the industry.
Big Data Analytics and Predictive Analytics in Healthcare
Big data analytics and predictive analytics play a crucial role in shaping the future of healthcare by leveraging data insights to improve decision-making, identify health trends, and enhance patient outcomes.
Significance of Big Data Analytics in Healthcare Decision-Making
Big data analytics in healthcare involves the analysis of large and complex data sets to extract valuable insights that can be used to make informed decisions. By utilizing advanced analytics tools, healthcare providers can identify patterns, trends, and correlations in data that may not be apparent through traditional methods
This enables more personalized treatment plans, improved operational efficiency, and better patient outcomes.
Examples of Predictive Analytics in Identifying Health Trends
Predictive analytics utilizes historical data to forecast future trends and outcomes in healthcare. For example, healthcare organizations can use predictive analytics to anticipate patient admissions, identify individuals at risk of developing certain conditions, or optimize resource allocation. By analyzing data from various sources, predictive analytics can help healthcare professionals proactively address potential issues and deliver more effective care.
Ethical Considerations in the Use of Big Data in Healthcare
While big data analytics offers numerous benefits in healthcare, it also raises ethical concerns regarding data privacy, security, and patient consent. Healthcare organizations must ensure that data is collected, stored, and analyzed in compliance with regulations such as HIPAA to protect patient confidentiality.
Additionally, there is a need for transparency and accountability in how data is used to prevent misuse or discrimination. Ethical considerations are crucial in maintaining patient trust and upholding the integrity of healthcare data analytics.
Cybersecurity Measures in Health Information Technology
Cybersecurity in health information technology plays a crucial role in protecting sensitive patient information from unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyber threats. As healthcare organizations increasingly rely on digital platforms to store and manage patient data, the need for robust cybersecurity measures becomes more evident.
Common Cybersecurity Threats in Healthcare
- Phishing Attacks: Cybercriminals use deceptive emails or messages to trick healthcare employees into revealing sensitive information or installing malware.
- Ransomware: Malicious software that encrypts data and demands payment for decryption, posing a significant threat to healthcare organizations.
- Insider Threats: Employees or contractors with access to sensitive data may intentionally or unintentionally compromise security measures.
- Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks: Overloading a system or network to disrupt services, causing potential harm to patient care.
Advancements in Cybersecurity Technology
- Endpoint Security: Implementing solutions to secure devices like computers, tablets, and smartphones that access healthcare networks.
- Multi-Factor Authentication: Adding an extra layer of security by requiring more than just a password for access.
- Encryption: Protecting data by encoding it in a way that only authorized parties can decipher.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Monitoring and analyzing security events in real-time to detect and respond to potential threats.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) in Healthcare

Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) technologies are revolutionizing the healthcare industry by providing innovative solutions for medical training, patient care, and surgical procedures. These technologies offer immersive experiences that enhance medical procedures and improve patient outcomes.
Applications of AR and VR in Medical Training and Patient Care
- AR and VR are used in medical training to simulate realistic scenarios for medical students and professionals, allowing them to practice in a safe and controlled environment.
- In patient care, AR and VR can be utilized to create personalized treatment plans, provide patient education, and offer virtual therapy sessions for rehabilitation.
Examples of How AR and VR Enhance Surgical Procedures
- Surgeons can use AR and VR technologies to visualize patient anatomy in 3D before performing surgeries, improving precision and reducing risks.
- During surgeries, AR can overlay important information directly onto the surgeon's field of view, such as vital signs or surgical instructions, enhancing efficiency and accuracy.
Potential Future Developments of AR and VR in Healthcare
- Future advancements in AR and VR may include the integration of AI algorithms to provide real-time feedback during medical procedures, helping healthcare professionals make informed decisions.
- AR and VR could also play a significant role in telemedicine by enabling remote consultations with immersive experiences, enhancing the quality of care for patients in remote locations.
Cloud Computing Solutions for Healthcare Providers
Cloud computing offers numerous benefits for healthcare providers, allowing them to store and access health data securely and efficiently. By utilizing cloud-based systems, healthcare organizations can streamline operations, improve collaboration among healthcare professionals, enhance patient care, and reduce costs associated with traditional IT infrastructures.
Benefits of Cloud Computing for Storing and Accessing Health Data
- Increased flexibility and scalability: Healthcare providers can easily scale their IT resources up or down based on their needs, without the need for large upfront investments in hardware.
- Improved accessibility: Health data can be accessed from any location at any time, enabling healthcare professionals to make faster and more informed decisions.
- Enhanced security: Cloud providers employ advanced security measures to protect sensitive health information, ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations.
- Cost-efficiency: Cloud computing eliminates the need for on-premises infrastructure maintenance, leading to cost savings for healthcare organizations.
Different Cloud Computing Solutions Available for Healthcare Providers
- Public Cloud: Offers a cost-effective solution with resources shared among multiple organizations.
- Private Cloud: Provides a dedicated and secure environment for healthcare providers, ensuring greater control over data and compliance requirements.
- Hybrid Cloud: Combines elements of public and private clouds, allowing healthcare organizations to leverage the benefits of both models.
- Multi-Cloud: Involves using multiple cloud providers to avoid vendor lock-in and optimize performance and cost.
Challenges of Transitioning to Cloud-Based Systems in Healthcare
- Data Security Concerns: Healthcare providers must address security risks associated with storing sensitive health information in the cloud.
- Compliance Issues: Ensuring compliance with regulations such as HIPAA when moving data to the cloud can be complex and requires careful planning.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Healthcare organizations may face challenges integrating cloud solutions with legacy systems and workflows.
- Reliability and Performance: Dependence on internet connectivity and cloud service providers for data access can impact system reliability and performance.
Patient-Centric Healthcare Technology Innovations
Designing healthcare technology with a focus on patient needs is crucial in providing quality care and improving outcomes. Patient-centric innovations aim to enhance the patient experience, increase engagement, and promote better health management.
Examples of Patient-Centric Technologies
- Mobile Health Apps: Apps that allow patients to track their health data, communicate with healthcare providers, schedule appointments, and access educational resources.
- Personal Health Records (PHRs): Online platforms where patients can store and manage their medical information, including lab results, medications, and treatment plans.
- Virtual Health Assistants: AI-driven assistants that provide personalized health advice, medication reminders, and support for managing chronic conditions.
Personalized Healthcare Solutions
Personalized healthcare solutions are revolutionizing medical treatment by tailoring interventions to individual patients' needs, preferences, and genetic makeup. This approach allows for more targeted and effective care, leading to better outcomes and patient satisfaction.
Final Review
As we wrap up our discussion on the Top 10 Trends in Health Information Technology for 2025, it's evident that the future of healthcare is intertwined with innovation and technology. These trends hold the promise of improving patient outcomes, streamlining processes, and enhancing overall healthcare delivery.
The road ahead is exciting, and these trends are paving the way for a new era in healthcare.
Quick FAQs
How can AI and machine learning benefit healthcare in 2025?
AI and machine learning can enhance diagnostics, personalize treatment plans, and streamline administrative tasks, ultimately improving patient care and outcomes.
What are the key challenges of integrating blockchain in healthcare by 2025?
The challenges include data privacy concerns, regulatory compliance, and interoperability issues between different blockchain platforms.
Why is patient-centric healthcare technology important for the future?
Designing technology around patient needs can lead to improved engagement, better adherence to treatment plans, and ultimately, better health outcomes for patients.